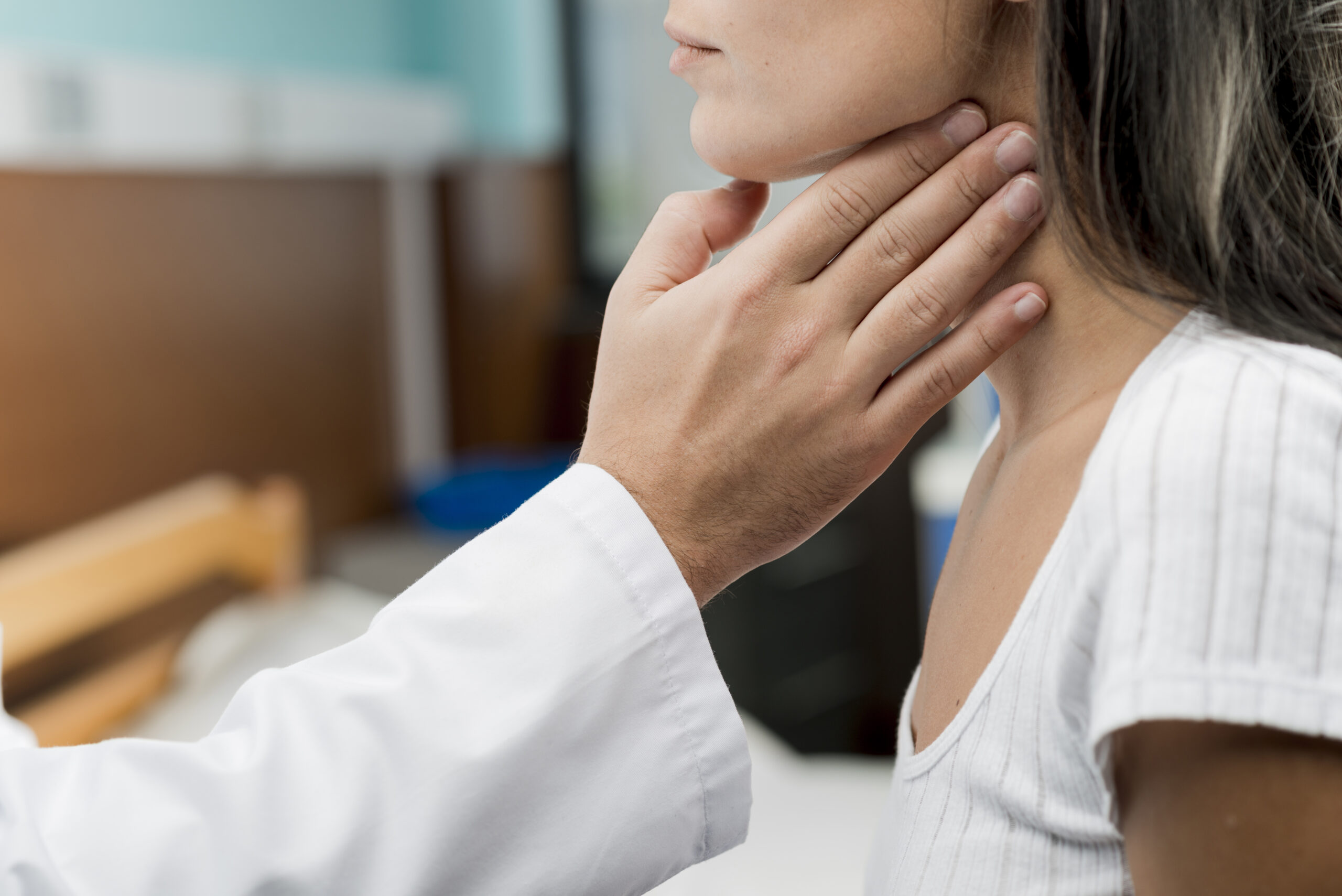
Feeling tired even after a full night’s sleep? Sudden weight changes without any clear reason? Mood swings, hair fall, or irregular periods? These could be signs of an underlying thyroid issue; something many people ignore until symptoms start interfering with daily life.
Thyroid disorders are more common than most people realize, especially in India. The thyroid may be small, but it plays a powerful role in regulating how the body functions. Understanding thyroid problems, recognizing the early symptoms of thyroid issues, and knowing when to seek medical care can make a significant difference in long-term health.
This guide breaks down thyroid disorders in a simple and easy-to-understand way, so you know what to look out for and when to take action.
What Is the Thyroid and Why Is It Important?
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland located at the front of the neck. It produces hormones that control metabolism, the process that determines how your body uses energy. These hormones influence heart rate, body temperature, digestion, mood, and even menstrual cycles.
When the thyroid produces too little or too much hormone, the body’s balance is disturbed, leading to various health issues collectively referred to as thyroid problems.
Thyroid Problems: Understanding the Two Main Types
Most thyroid disorders fall into two broad categories:
- Hypothyroidism
This occurs when the thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones, slowing down bodily functions.
2. Hyperthyroidism
This happens when the thyroid gland produces excess hormones, speeding up the body’s processes.
Knowing the difference between hypo and hyperthyroidism is key to understanding symptoms and treatment options.
Early Symptoms of Thyroid Problems You Should Not Ignore
Thyroid disorders often develop slowly, and early signs can be subtle. Because symptoms may resemble stress or lifestyle issues, many people delay seeking medical advice.
Common early symptoms of thyroid problems include:
- Unexplained fatigue
- Weight changes without diet or activity changes
- Hair thinning or hair fall
- Dry skin or excessive sweating
- Mood changes such as anxiety or depression
- Sensitivity to cold or heat
- Irregular menstrual cycles
- Changes in heart rate
- Difficulty concentrating
If several of these symptoms persist, it’s important to consider a thyroid evaluation.
Hypothyroidism Symptoms: When the Body Slows Down
Hypothyroidism is one of the most common thyroid disorders, particularly among women. When thyroid hormone levels are low, the body’s systems begin to slow.
Common hypothyroidism symptoms include:
- Constant tiredness or low energy
- Weight gain despite normal eating habits
- Dry, coarse skin
- Hair loss or thinning eyebrows
- Feeling cold even in warm environments
- Constipation
- Depression or low mood
- Slow heart rate
- Heavy or irregular menstrual periods
- Puffiness of the face or eyes
Because these symptoms develop gradually, many people live with hypothyroidism for years without diagnosis.
Hyperthyroidism Symptoms: When the Body Speeds Up
Hyperthyroidism causes the body to function faster than normal, often leading to noticeable physical and emotional changes.
Common hyperthyroidism symptoms include:
- Sudden or unexplained weight loss
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Excessive sweating
- Heat intolerance
- Nervousness or anxiety
- Tremors in hands
- Difficulty sleeping
- Increased appetite
- Frequent bowel movements
- Muscle weakness
- Irregular or lighter menstrual cycles
These symptoms can feel overwhelming and may significantly affect quality of life if left untreated.
Difference Between Hypo and Hyperthyroidism Explained Simply
Understanding the difference between hypo and hyperthyroidism helps identify which condition may be affecting you.
In hypothyroidism, the thyroid is underactive, causing the body to slow down. Energy levels drop, weight increases, and people often feel cold, tired, and low.
In hyperthyroidism, the thyroid is overactive, pushing the body into overdrive. Heart rate increases, weight drops, anxiety rises, and the person may feel constantly warm or restless.
Although opposite in nature, both conditions require proper diagnosis and long-term management.
What Causes Thyroid Problems?
Several factors can contribute to thyroid disorders, including:
- Autoimmune conditions such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis or Graves’ disease
- Iodine deficiency or excess
- Genetic predisposition
- Hormonal changes during pregnancy or menopause
- Certain medications
- Chronic stress
- Radiation exposure to the neck
Women are more likely to develop thyroid disorders, particularly during hormonal transitions.
How Are Thyroid Disorders Diagnosed?
Diagnosis usually involves:
- Blood tests to measure thyroid hormone levels (T3, T4, TSH)
- Physical examination of the neck
- Imaging tests if nodules or swelling are suspected
Early diagnosis allows for effective treatment and prevents complications affecting the heart, bones, fertility, and mental health.
When Should You Seek Medical Care?
You should consult a doctor if:
- Symptoms persist for several weeks
- Daily activities are affected
- There is a family history of thyroid disease
- You experience sudden weight changes
- Menstrual cycles become irregular
- Heart rate feels abnormal
- You notice swelling in the neck area
Prompt medical evaluation ensures better control and long-term well-being.
Living Well With Thyroid Disorders
With proper treatment, most people with thyroid conditions live healthy, active lives. Management may include:
- Regular medication
- Periodic blood tests
- Lifestyle adjustments
- Balanced diet
- Stress management
- Routine follow-ups
Consistency in treatment is essential; stopping medication without medical advice can worsen symptoms.
Listen to Your Body, Act Early
Thyroid disorders may be common, but they are often misunderstood and overlooked. Recognising thyroid problems, understanding hypothyroidism symptoms, hyperthyroidism symptoms, and spotting the early symptoms of thyroid problems can prevent long-term complications.
Knowing the difference between hypo and hyperthyroidism empowers you to seek the right care at the right time. If something feels off, trust your instincts; your body often gives early signals before serious issues arise.
Early diagnosis, proper treatment, and regular monitoring can restore balance and protect your overall health.